Calculate the Average Dose and the dose rate dispersion
Source:R/calc_AverageDose.R
calc_AverageDose.RdThis functions calculates the Average Dose and its extrinsic dispersion, estimating the standard errors by bootstrapping based on the Average Dose Model by Guérin et al., 2017.
sigma_m
The program requires the input of a known value of sigma_m,
which corresponds to the intrinsic overdispersion, as determined
by a dose recovery experiment. Then the dispersion in doses (sigma_d)
will be that over and above sigma_m (and individual uncertainties sigma_wi).
Usage
calc_AverageDose(
data,
sigma_m,
Nb_BE = 500,
na.rm = TRUE,
plot = TRUE,
verbose = TRUE,
...
)Arguments
- data
RLum.Results or data.frame (required): for data.frame: two columns with
De(data[,1])andDe error(values[,2])- sigma_m
numeric (required): the overdispersion resulting from a dose recovery experiment, i.e. when all grains have received the same dose. Indeed in such a case, any overdispersion (i.e. dispersion on top of analytical uncertainties) is, by definition, an unrecognised measurement uncertainty.
- Nb_BE
integer (with default): sample size used for the bootstrapping
- na.rm
logical (with default): exclude NA values from the data set prior to any further operation.
- plot
logical (with default): enable/disable the plot output.
- verbose
logical (with default): enable/disable output to the terminal.
- ...
further arguments that can be passed to graphics::hist. As three plots are returned all arguments need to be provided as list, e.g.,
main = list("Plot 1", "Plot 2", "Plot 3"). Note: not all arguments ofhistare supported, but the output ofhistis returned and can be used of own plots.Further supported arguments:
mtext(character),rug(TRUE/FALSE).
Value
The function returns numerical output and an (optional) plot.
———————————–[ NUMERICAL OUTPUT ]
———————————–RLum.Results-object
slot: @data
[.. $summary : data.frame]
| Column | Type | Description |
| AVERAGE_DOSE | numeric | the obtained average dose |
| AVERAGE_DOSE.SE | numeric | the average dose error |
| SIGMA_D | numeric | sigma |
| SIGMA_D.SE | numeric | standard error of the sigma |
| IC_AVERAGE_DOSE.LEVEL | character | confidence level average dose |
| IC_AVERAGE_DOSE.LOWER | character | lower quantile of average dose |
| IC_AVERAGE_DOSE.UPPER | character | upper quantile of average dose |
| IC_SIGMA_D.LEVEL | integer | confidence level sigma |
| IC_SIGMA_D.LOWER | character | lower sigma quantile |
| IC_SIGMA_D.UPPER | character | upper sigma quantile |
| L_MAX | character | maximum likelihood value |
[.. $dstar : matrix]
Matrix with bootstrap values
[.. $hist : list]
Object as produced by the function histogram
————————[ PLOT OUTPUT ]
————————
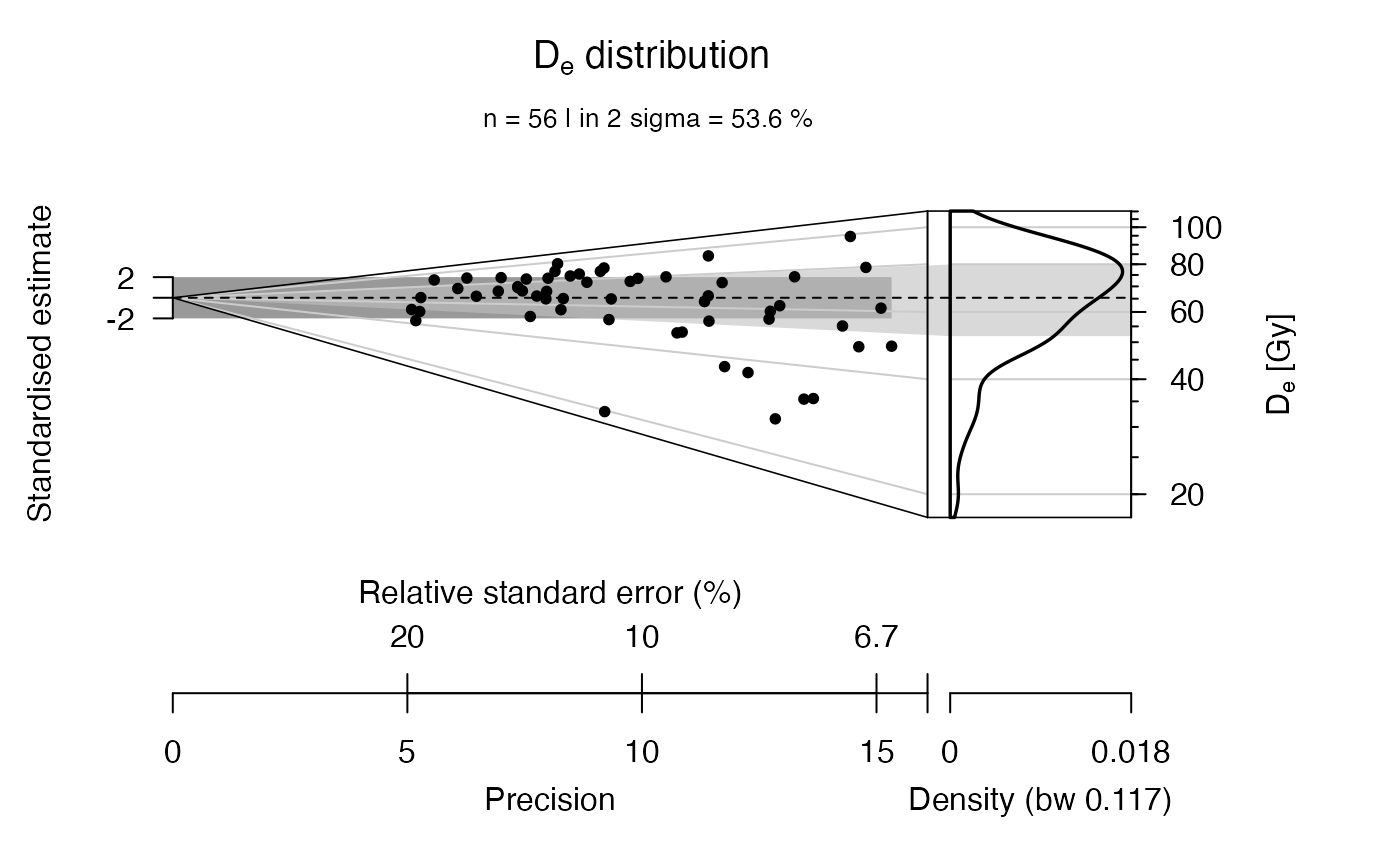
The function returns two different plot panels.
(1) An abanico plot with the dose values
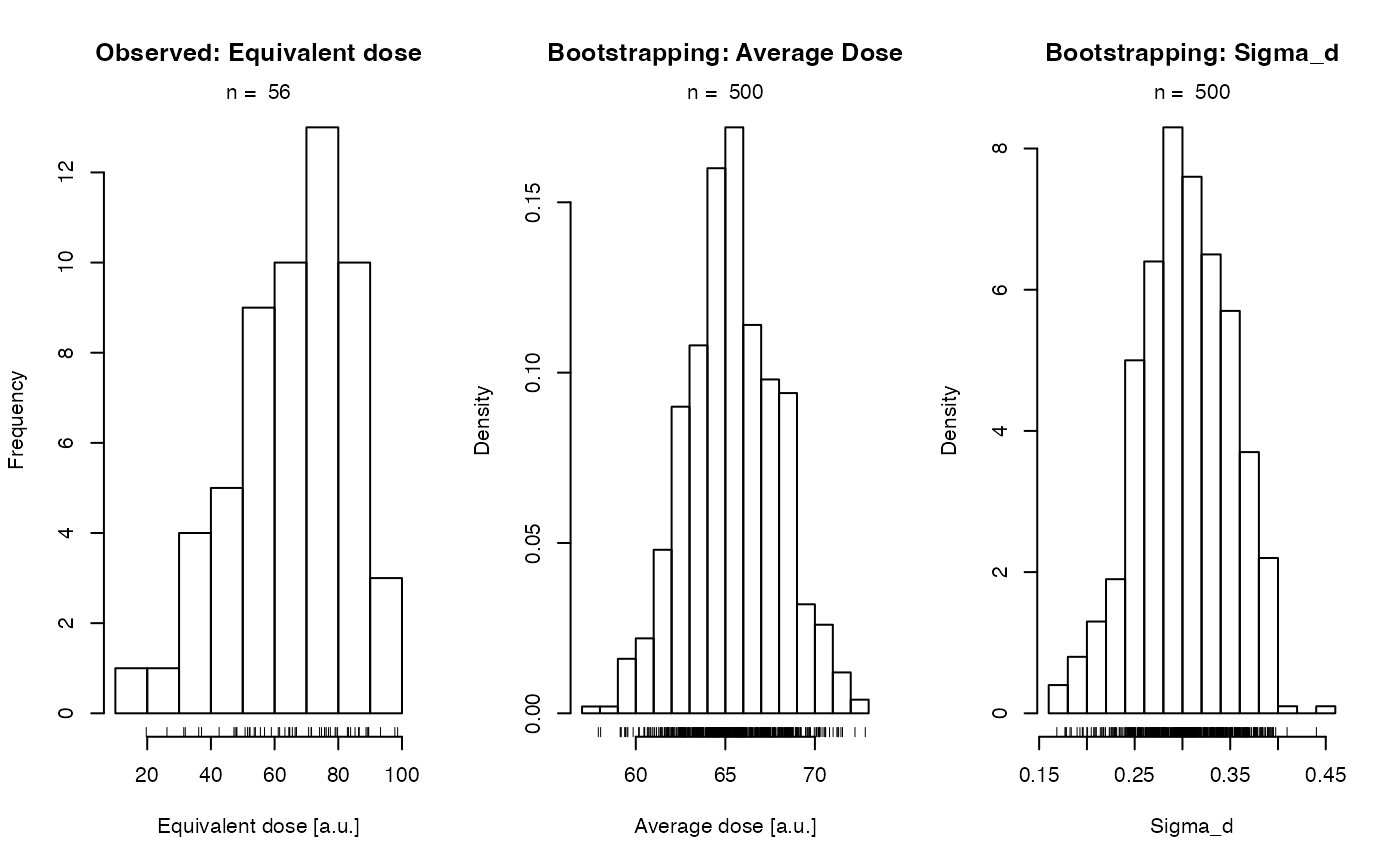
(2) A histogram panel comprising 3 histograms with the equivalent dose and the bootstrapped average dose and the sigma values.
How to cite
Christophe, C., Philippe, A., Guérin, G., Kreutzer, S., 2025. calc_AverageDose(): Calculate the Average Dose and the dose rate dispersion. Function version 0.1.6. In: Kreutzer, S., Burow, C., Dietze, M., Fuchs, M.C., Schmidt, C., Fischer, M., Friedrich, J., Mercier, N., Philippe, A., Riedesel, S., Autzen, M., Mittelstrass, D., Gray, H.J., Galharret, J., Colombo, M., Steinbuch, L., Boer, A.d., 2025. Luminescence: Comprehensive Luminescence Dating Data Analysis. R package version 1.1.2. https://r-lum.github.io/Luminescence/
References
Guérin, G., Christophe, C., Philippe, A., Murray, A.S., Thomsen, K.J., Tribolo, C., Urbanova, P., Jain, M., Guibert, P., Mercier, N., Kreutzer, S., Lahaye, C., 2017. Absorbed dose, equivalent dose, measured dose rates, and implications for OSL age estimates: Introducing the Average Dose Model. Quaternary Geochronology 1-32. doi:10.1016/j.quageo.2017.04.002
Further reading
Efron, B., Tibshirani, R., 1986. Bootstrap Methods for Standard Errors, Confidence Intervals, and Other Measures of Statistical Accuracy. Statistical Science 1, 54-75.
Author
Claire Christophe, IRAMAT-CRP2A, Université de Nantes (France), Anne Philippe, Université de Nantes, (France), Guillaume Guérin, IRAMAT-CRP2A, Université Bordeaux Montaigne, (France), Sebastian Kreutzer, Institute of Geography, Heidelberg University (Germany) , RLum Developer Team
Examples
##Example 01 using package example data
##load example data
data(ExampleData.DeValues, envir = environment())
##calculate Average dose
##(use only the first 56 values here)
AD <- calc_AverageDose(ExampleData.DeValues$CA1[1:56,], sigma_m = 0.1)
#>
#> [calc_AverageDose()]
#>
#> >> Initialisation <<
#> n: 56
#> delta: 65.79393
#> sigma_m: 0.1
#> sigma_d: 0.2861594
#>
#> >> Calculation <<
#> log likelihood: -19.251
#>
#> confidence intervals
#> --------------------------------------------------
#> IC_delta IC_sigma_d
#> level 0.95 0.9500
#> CredibleIntervalInf 60.40 0.2077
#> CredibleIntervalSup 69.74 0.3860
#> --------------------------------------------------
#>
#> >> Results <<
#> ----------------------------------------------------------
#> Average dose: 65.3597 se(Aver. dose): 2.4669
#> sigma_d: 0.3092 se(sigma_d): 0.0476
#> ----------------------------------------------------------
 ##plot De and set Average dose as central value
plot_AbanicoPlot(
data = ExampleData.DeValues$CA1[1:56,],
z.0 = AD$summary$AVERAGE_DOSE)
##plot De and set Average dose as central value
plot_AbanicoPlot(
data = ExampleData.DeValues$CA1[1:56,],
z.0 = AD$summary$AVERAGE_DOSE)