Run Monte-Carlo Simulation for TL (localized transitions)
Source:R/run_MC_TL_LOC.R
run_MC_TL_LOC.RdRuns a Monte-Carlo (MC) simulation of thermoluminescence (TL) using the generalized one trap (GOT) model. Localized transitions refer to transitions which do not involve the conduction or valence band. These transitions take place between the ground state and an excited state of the trapped charge, and also involve an energy state of the recombination centre. The heating rate in this function is assumed to be 1 K/s.
Usage
run_MC_TL_LOC(
s,
E,
times,
b = 1,
clusters = 10,
n_filled = 100,
r,
method = "par",
output = "signal",
...
)Arguments
- s
numeric (required): The frequency factor of the trap (s^-1)
- E
numeric (required): Thermal activation energy of the trap (eV)
- times
numeric (required): The sequence of temperature steps within the simulation (s). The default heating rate is set to 1 K/s. The final temperature is
max(times) * b- b
numeric (with default): the heating rate in K/s
- clusters
numeric (with default): The number of created clusters for the MC runs. The input can be the output of create_ClusterSystem. In that case
n_filledindicate absolute numbers of a system.- n_filled
integer (with default): The number of filled electron traps at the beginning of the simulation (dimensionless). Can be a vector of
length(clusters), shorter values are recycled.- r
numeric (required): The localized retrapping ratio (dimensionless)
- method
character (with default): Sequential
'seq'or parallel'par'processing. In the parallel mode the function tries to run the simulation on multiple CPU cores (if available) with a positive effect on the computation time.- output
character (with default): output is either the
'signal'(the default) or'remaining_e'(the remaining charges/electrons in the trap)- ...
further arguments, such as
coresto control the number of used CPU cores orverboseto silence the terminal
Value
This function returns an object of class RLumCarlo_Model_Output which
is a list consisting of an array with dimension length(times) x clusters
and a numeric time vector.
Details
The model
$$ I_{LOC}(t) = -dn/dt = (s * exp(-E/(k_{B} * T))) * (n^2 / (r + n)) $$
Where in the function:
E := the thermal activation energy (eV)
s := the frequency factor for the trap (s^-1)
t := time (s)
\(k_{B}\) := Boltzmann constant (8.617 x 10^-5 eV K^-1)
T := temperature (°C)
n := the instantaneous number of electrons
r := the retrapping ratio for localized transitions
How to cite
Kreutzer, S., 2025. run_MC_TL_LOC(): Run Monte-Carlo Simulation for TL (localized transitions). Function version 0.1.0. In: Friedrich, J., Kreutzer, S., Pagonis, V., Schmidt, C., 2025. RLumCarlo: Monte-Carlo Methods for Simulating Luminescence Phenomena. R package version 0.1.10. https://r-lum.github.io/RLumCarlo/
References
Pagonis, V., Friedrich, J., Discher, M., Müller-Kirschbaum, A., Schlosser, V., Kreutzer, S., Chen, R. and Schmidt, C., 2019. Excited state luminescence signals from a random distribution of defects: A new Monte Carlo simulation approach for feldspar. Journal of Luminescence 207, 266–272. doi:10.1016/j.jlumin.2018.11.024
Examples
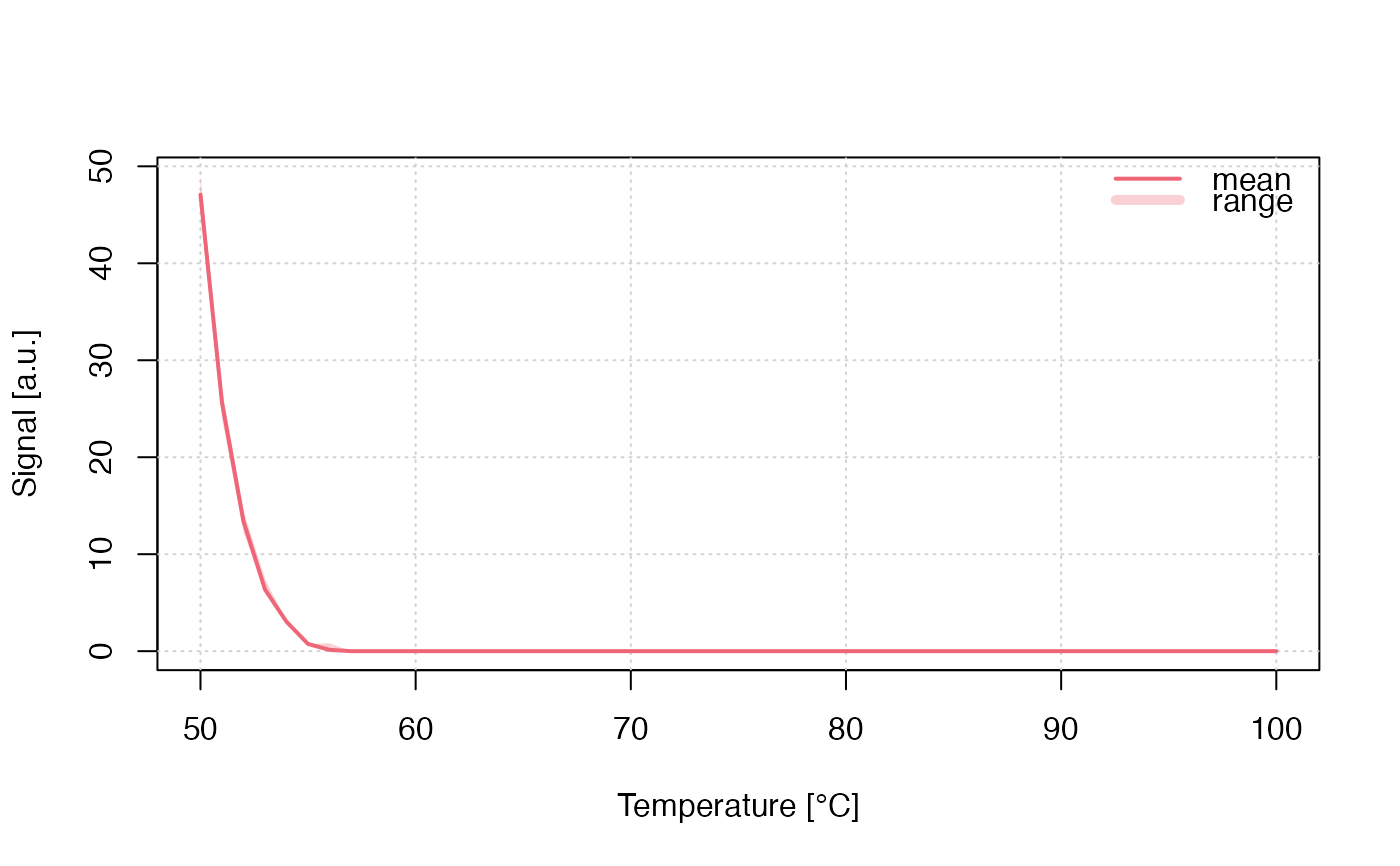
## the short example
run_MC_TL_LOC(
s = 1e14,
E = 0.9,
times = 50:100,
b = 1,
method = "seq",
clusters = 30,
r = 1) %>%
plot_RLumCarlo()
 if (FALSE) { # \dontrun{
## the long (meaningful) example
results <- run_MC_TL_LOC(
s = 1e14,
E = 0.9,
times = 50:100,
method = "par",
clusters = 100,
r = 1)
## plot
plot_RLumCarlo(results)
} # }
if (FALSE) { # \dontrun{
## the long (meaningful) example
results <- run_MC_TL_LOC(
s = 1e14,
E = 0.9,
times = 50:100,
method = "par",
clusters = 100,
r = 1)
## plot
plot_RLumCarlo(results)
} # }